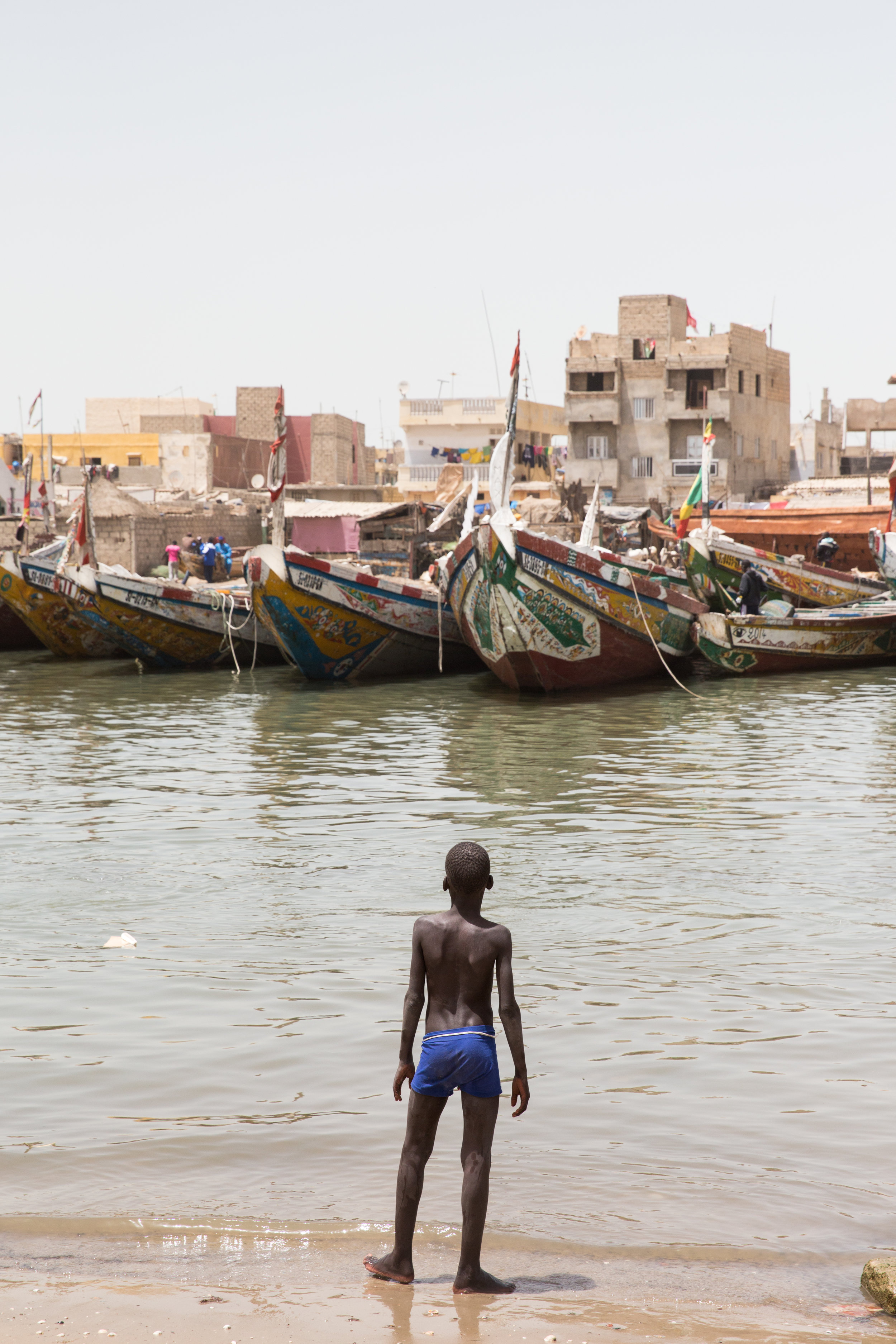It's Already Happening
Stay Wild
Story and Photography by Greta Rybus // @gretarybus
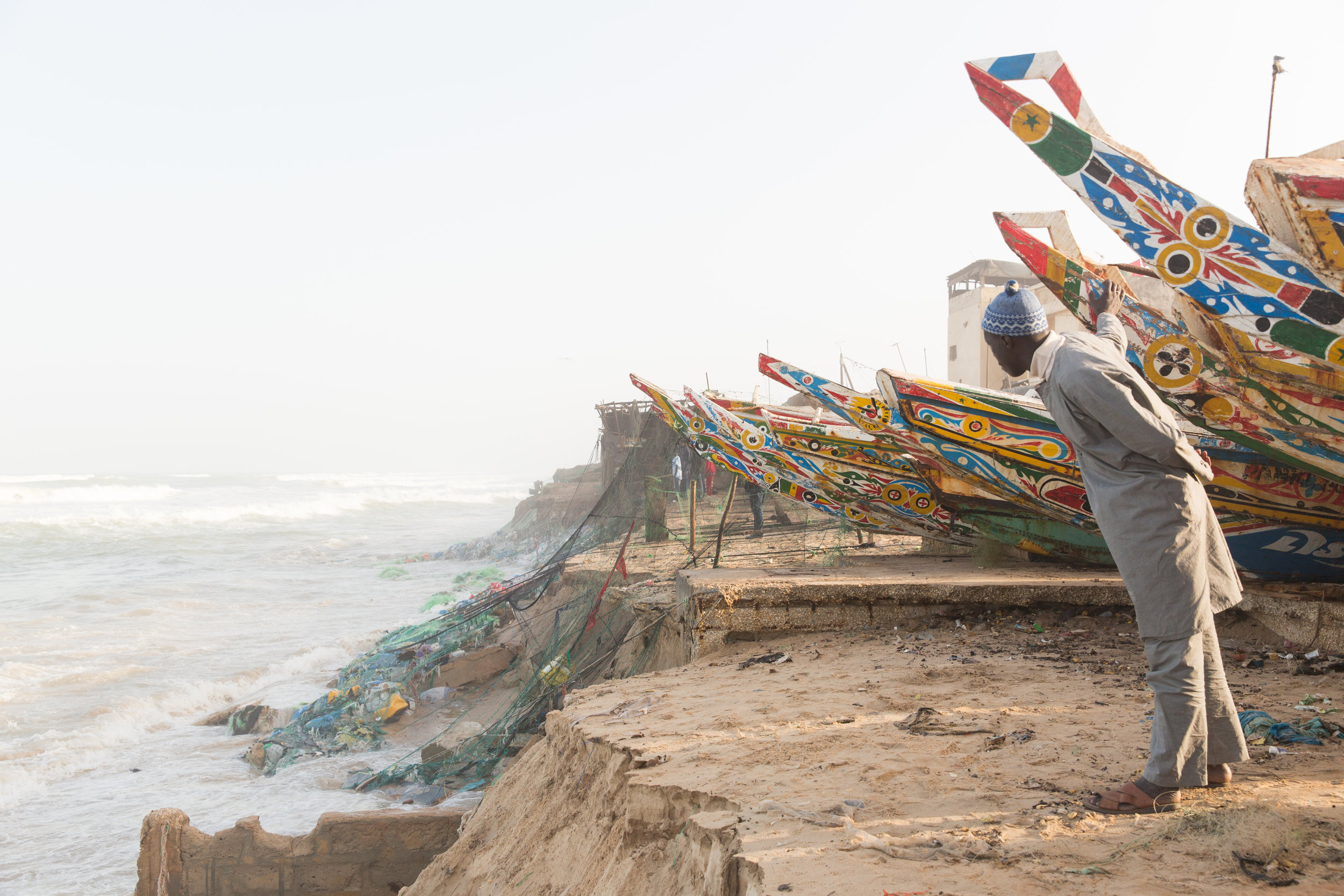
The fishermen in the bustling fishing community Guet Ndar once dragged their boats for an hour across the sand before reaching the sea. Now the ocean laps at their front door and eats their homes in giant, crumbling gulps. Inland, in a little village called Takhembeut, the herders and farmers once relied on the rainy season’s punctuality, the timely arrival of just enough water to sustain crop and cattle.
The UN recognized Saint Louis, called Ndar by locals, as being the city most threatened by climate change in Africa. At the northernmost point of Senegal, Ndar hugs the Sahara and hovers on the edge of the Arabic and African worlds. The locals are knowledgeable about climate—being from the desert means paying close attention to the rains and to the seas. Even the younger workers have been in the fields or on the seas for many years, doing the work of their fathers or grandmothers who taught them to pay attention, notice change, and anticipate what comes next.
The last few years have brought variables greater than anyone anticipated. Winds and waters have changed, causing coastal erosion along Senegal’s coast, made worse in Ndar by a botched canal project intended to slow the rising water. The rainy season is shorter and more erratic. The herders can no longer grow crops for their animals, and now shake seed pods from the trees to sustain their shrinking herds. The farmers grow just enough food for their families, and many have become the first in their lineage to supplement their work with odd jobs in the city.
The Senegalese government is paying attention. They are building housing for the fishermen who are losing their homes to the sea. They are providing municipal water, enough to drink and bathe in, for the families who live inland. But this is not a problem caused by the Senegalese. It’s a problem larger than a people or a country. It is a problem caused by an anemic global response to climate change. It is caused by larger countries making policy and industrial decisions that impact global health. For those who rely directly on natural resources for survival, like the majority of Senegalese people, climate change will be a calamitous test and a catalyst for poverty worldwide.
“The waves of the sea were very strong, strong enough to cross over the protective wall and reach up to my house. My house was flooded. I changed the gate to the other side of the home, and put sand bags on the sea facing side.”
— Baye Sarr, fishing boat captain
“Coastal erosion is undoubtedly related to rising sea level. As a consequence of the relative rise in the temperature worldwide, the icecaps are melting, bringing about a rise in the ocean level. In low altitude areas, like Saint Louis, these phenomena cause an overflowing called marine flooding.”
— Abou Sy, climate change scientist and geographer
“Climate change is upsetting the balance of the seasons. However, even though some fishermen may feel reluctant to go out fishing when they notice that weather conditions are not suitable to catch a lot of fish, others go out anyway, since they don’t have another source of income. The seasons are no longer regular; the fishermen are experiencing this upside down weather day-in and day-out. Nowadays, they happen to go out under good weather conditions, but once they are in the middle of the ocean, strong winds and waves suddenly surround them, jeopardize their activities, and even put their lives in danger. In my opinion, climate change is to be blamed for this imbalance.”
— Boly Sarr, retired fishing captain
“Of course, I have seen homes falling into the ocean. We can cope with the climate conditions in this area because we were born and brought up here. We experienced all the changes that have happened over time. We cannot live outside the coastal area. If we relocate inland we won’t be able to adapt. We are just like fish in the water.”
— Ndiawar, community leader and retired fisherman
“Developed countries are the major greenhouse gases issuers and the main cause of climate change. In developing countries, people discuss climate change more and more because they are directly affected by its impact. The population is mainly made up of farmers, herders and fishermen, and they are most vulnerable to climate change. Climate change is increasing poverty. It is not the only cause of the poverty, but it is accelerating it. Unfortunately, we don’t have the choice but to adapt to a phenomenon we didn’t cause.”
— Abdou Sy, climate change scientist and geographer